Armée
iranienne
Branches militaires: Les forces régulières de
la République
Islamique d'Iran incluent l'armée de terre (Artesh),
la marine (Niru-Daryai), l'armée de l'air (Niru-Havayi)
et les forces de défense aériennes. La force
parallèle des Gardiens de la
révolution islamique incluent des compositions terrestres,
aériennes et navales ainsi que les forces Qods
(Forces spéciales) et la milice des Basij.
D'autres groupes paramilitaires peuvent aussi être
mobilisés.
Les capacités militaires de l'Iran sont pour la plupart
tenues
secrètes, mais ses possibilités et technologies
relativement avancées
sont démontrées par la construction de missiles longue
portée comme le Shahab-3 et par la modification d'armements
acheté sous licence.
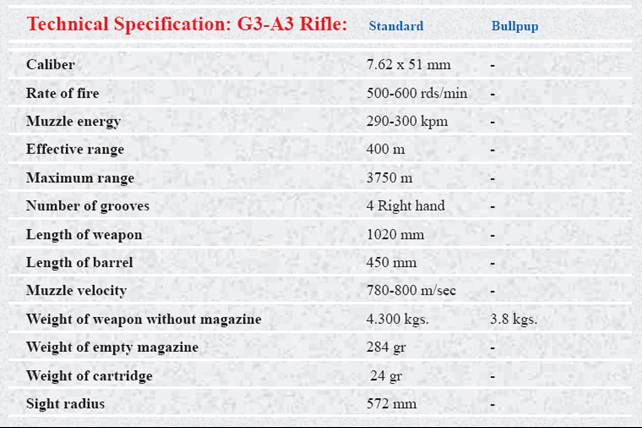
Les forces armées iraniennes ont un effectif total de 755 000 soldats
(à titre de comparaison, l'armée française compte
en 2005 350 000 hommes).
Dans le détail, l'armée iranienne est composée
de trois branches :
L'Iran peut aussi compter sur 1 600 véhicules blindés,
300 avions de combat et 3 sous-marins.
L'armée régulière est doublée par la
force des Pasdarans qui dispose de 230 000hommes dans une
vingtaine de grande formations, dont des unités parachutistes, d’opérations spéciales ou d’infanterie de marine.
Gardiens de la Révolution islamique
Le Corps des Gardiens de la révolution islamique (en persan :
سپاه پاسداران انقلاب اسلامى,
Sepah-e Pasdaran-e Enghelāb-e Islami), souvent appelé Gardiens
de la Révolution (abrévié GRI) ou
encore appelé par son nom persan Sepah
(signifiant armée) ou Pasdaran, est une
organisation militaire de la République islamique d'Iran.
Le Sepah-e Pasdaran est séparé de l'armée
iranienne régulière et lui
est parallèle. Ils sont très bien équipés
avec leur propre marine,
armée de l'air et forces terrestres. La force est aussi
responsable des
missiles d'Iran sur lesquels l'armée régulière n'a
aucun contrôle.
Des efforts récents ont été faits afin de
créer un commandement
conjoint entre l'armée régulière et les gardiens
de la révolution, mais
ils ont été limités par leur nature et n'ont pas
eu un impact très
grand.
Le corps des gardiens de la révolution a été
fondé par un décret du 5 mai 1979, en
tant que force loyale à l'Ayatollah Khomeini, mais sont ensuite
devenu une force armée à part entière pendant la Guerre Iran-Irak où l’utilisation
de ‘’vagues humaines ‘’ constituées très souvent d’adolescents
inexpérimentés contre l’armée Iraquienne
causèrent des pertes pour les GRI 2 fois supérieures
à celles de l’armée régulière.
En 2000, on estime que les GRI regroupent 130 000 hommes dans une
vingtaine de grandes formations, dont des unités parachutistes,
d’opérations spéciales ou d’infanterie de marine.
L'actuel commandant en chef du corps des gardiens de la
révolution islamique est le Major
Général Yahya Rahim Safavi, qui fut
précédé par Mohsen Rezaî. L'actuel
président d'Iran Mahmoud Ahmadinejad était
membre des gardiens de la révolution pendant la guerre Iran-Irak.
Département de
sécurité et de renseignement extérieurs
Cette structure spécifique des GRI pour les opérations
de renseignements
et d’actions clandestines gère différents services ou
cellules chargées
des opérations clandestines dans le monde entier (assassinats
d’opposants en autre).
Il est responsable des groupes ‘’Al-Qods’’,
cellules des Pasdarans opérant à l’étranger, qui
assurent la formation,
l’entraînement et parfois, l’encadrement des mouvements
extrémistes islamiques, comme en Bosnie-Herzégovine durant la
guerre civile dans ce pays, la formation des activistes kurdes
du PKK, ou
un soutien aux mouvements chi’ites iraquien dans la guerre en Iraq.
Implantation au Liban
Il dispose d'un quartier-général opérationnel
libanais à Ras al-Aïn
(Baalbek). L'une de ses fonctions est de piloter les activités
militaires hors d'Iran
Cinq commandements opérationnels sont situés à
Beyrouth-sud, Tyr,
Aïn Boussawr, Mlita (Djebel Safi) et Macheghara (Beka'a Ouest). Le
chef
au Liban est Assadalah Hadji Reza Asgar (" Abou Asager ")

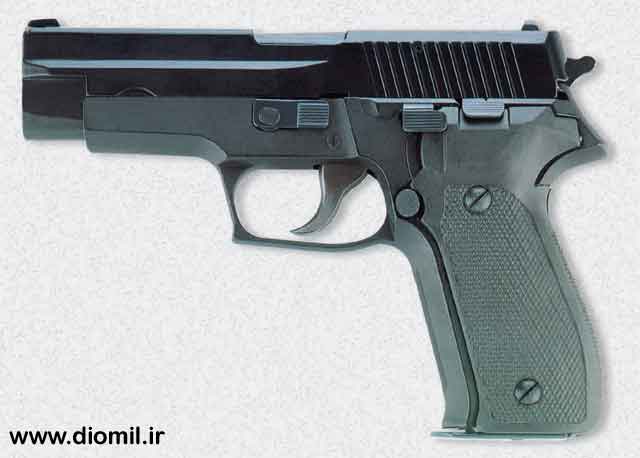
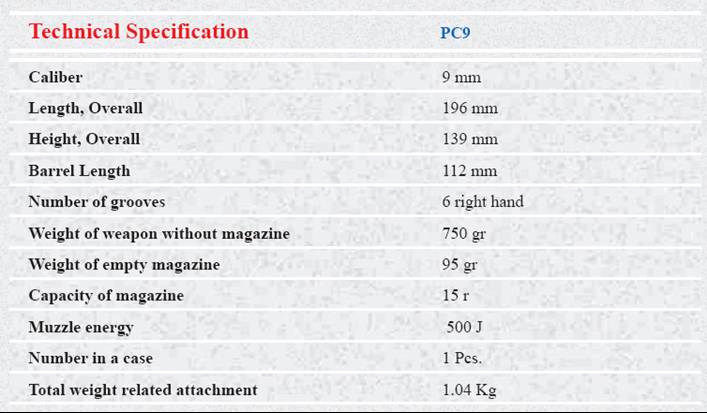
Pc9 Combat Pistol
The
PC9 mm pistol combat has been designed with advanced technology
specifically for military and law enforcement forces. This Pistol works
with short recoil and has double action trigger, automatic pin safety
lock, decoking lever with external slide catch. This pistol is
automatically loaded by magazine after firing of final shot the slide
is stopped.

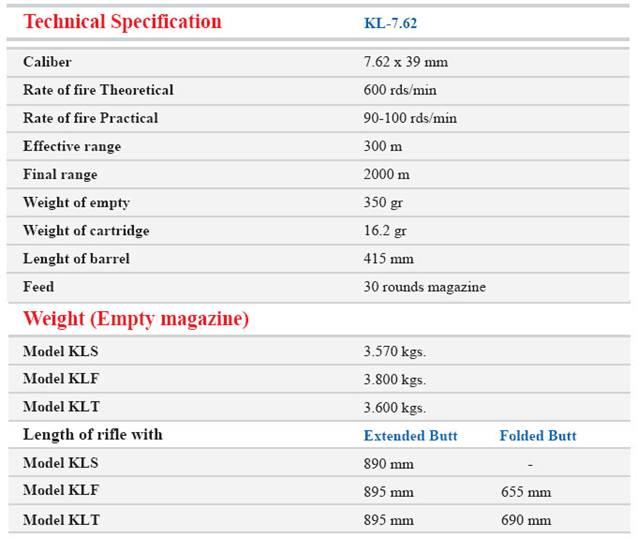
 RIFLE TYPE KL - 7.62 mm
RIFLE TYPE KL - 7.62 mm
The
Assault rifle type KL-7.62 mm is a gas-operated rifle and capable both
of semi-automatic and automatic fire and intended for destroying
hostile individual and group also can be in close combat by bayonet and
butt stock has become the weapon of all army forces especially suited
for the partisan war fares in every weather conditions.The rifle is
supplied in various types such as fixed butt stock (KLS), under folding
butt stock (KLF) & side
folding butt stock (KLT). Also it should be mentioned that the rifle
has a multi-purpose bayonet.

 Retractable Butt Stock (g3-a4)
Retractable Butt Stock (g3-a4)
This
requires a 7.62 mm x 51 propellant cartridge. A blank attachment
permits 7.62 x 51 blank ammunition to be fired. The Rifle G3 is
available in three models.
 Fixed Butt Stock (g3-a3)
Fixed Butt Stock (g3-a3)
KH 2002, 5.56x 45 mm
The
KH-2002 is a 5.56 mm, automatic, gas operated, Bullpup assault rifle
and is designed for the unique requirements of various operation
missions.It uses a simple four stages fire mechanism, which provide
single shot, automatic fire, and three-round bursts. A selector lever
can activate safetyposition firearm. The top of carrying handle can
also be used to mount optical or nightsights
to provide the high fire accuracy. Extensive engineering works on
design of internal and external ballistics of KH-2002, ensures its
efficiency and high performance.

 Spg 9 Sub-rifle
Spg 9 Sub-rifle
The
advantages of training by SPG 9 sub-rifles (training aids) are: much
lower cost (saving real ammunitions), higher safety, coincides of
firing results as if real ammunition is employed, no wear out of
barrels, utilization of smaller fire field & time saving.

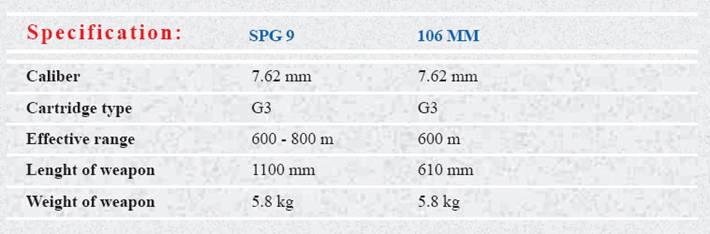
106 mm SUB-RIFLE
The advantages of training by 106 mm sub-rifles (training aids) are:
much lower cost (saving real ammunitions), higher safety, coincides of
firing results as if real ammunition is employed, no wear out of
barrels, utilization of smaller fire field & time saving.
The
light submachine gun MPT9K cal. 9 mm is an automatic weapon and can be
used for either single and bursts selectively from all shooting
positions. The weapon is loaded directly with pressure of powder gas.
This weapon is specially used in personal protection guards.

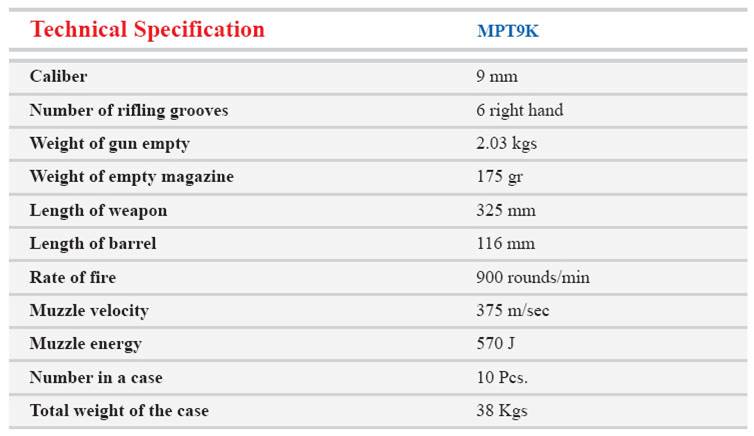
The
submachine gun MPT9 cal. 9 mm is an automatic weapon and can be used
for either single and bursts selectively from all shooting positions.
The weapon is loaded directly with pressure of power gas and its barrel
cooled with air. Cartridges are fed from 30 round box type magazine, in
order to carry the weapon easily and better usage it is usually
equipped with retractable butt stock, if required it can be replaced
with fix butt stock.



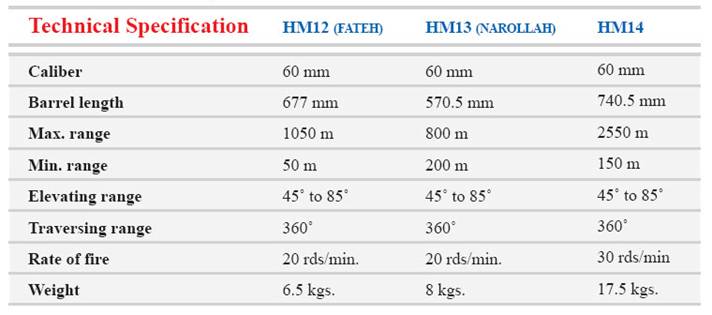
iranian made mortar LAUNCHERS
FATEH MORTAR LAUNCHERS and NAROLLAH MORTAR
LAUNCHERS and HM14 MORTAR LAUNCHERS
With its light weight and simple operation is as a portable weapons
group, and as far as its range is able to implement a large volume of
firing rapidly on targets. This mortar is designed to be applied on any
kinds of battle-fields and under any climate. This mortar is generally
operated by two persons but in urgent case it can be used by one as
well. The sight is simple and accurate and it remains in firm position
during firing.
81 mm HM15
Hadid 81mm mortar launchers are of unrifled and barrel-loading type
with 360o of firing field. Because of possessing high shooting angle,
this weapon enables to fire from behind of obstacles. In regions where
routs are impracticable, the mortar can be taken apart and carried by
infantry. Due to its simple structure, it can be erected and operated
only by two or three persons.
120 mm HM16
Hadid 120mm mortar launchers are of unrifled and barrel-loading type
with 360o of firing field. Because of possessing high shooting angle,
this weapon enables to fire from behind of obstacles. In regions where
routs are impracticable, the mortar can be taken apart and carried by
infantry. Due to its simple structure, it can be erected and operated
only by two or three persons.


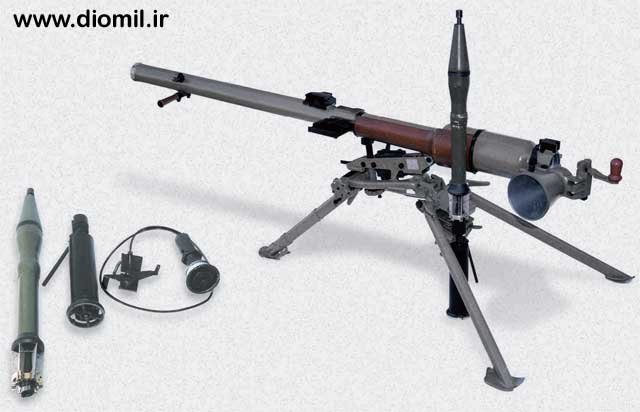
Anti-tank Gun Spg-9
Light
weight SPG9 Anti-Tank & anti armoured shelter weapon with high
penetration depth. The spare parts are completely compatible with
eastern model and also mountable on vehicle with special rotary stand
(optional) with high maneuverability.v


RPG 7 ANTI TANK ROCKET LAUNCHER and COMMANDO ROCKET LAUNCHER
The
light RPG 7 anti tank rocket launcher is a quite effective weapon
against Tanks, motion targets including any armoured ones,
fortification and artillery. This rocket launcher which lacks groove,
repulsion spring and cocking lever is equipped with barrel, firing
mechanism, flint hammer & sighting notch, high precision, little
weight, simple design and feasibility in any atmospheric conditions are
among some particularities of this weapon.

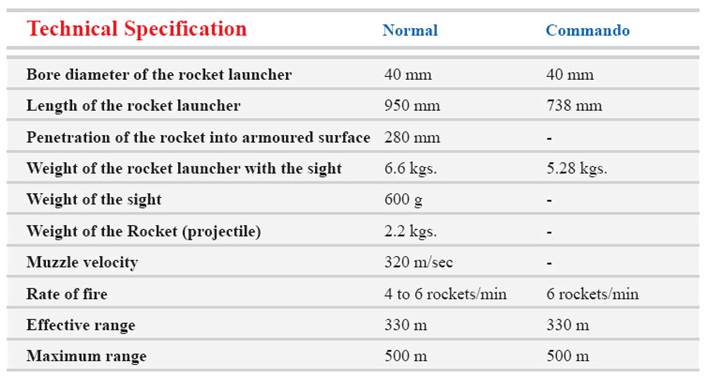

Single Barrel Launcher and Double BARREL LAUNCHER
A
super light rocket Launcher carried by only one man on foot, specially
used by irregular forces, usable in forests & mountains.



Nakhjir Sniper Rifle Svd
The
SVD is a well-designed, light-weight and well-built precision rifle
which generally uses in search and destroy missions from a long
distance.The rifle is a semi-automatic, gas-operated and air-cooled arm
with 10 rounds magazine and can be used with various optical and night
sights


Anti Aircraftmachine Gun
The
MGD-12.7 mm is an anti-aircraft machine gun, which applies repulsion
force of gunpowder gas for loading and ejection of the rounds. This gun
is designed for surface air firing purposes to aim at low altitude
flying or swooping aircrafts, parachutists, light armored targets and
other ground aims enemy.


Machine Gun Pkm-t80
The
PKM is a gas-operated and light machine gun which is intended for use
for regular and partisan war fares. The reasons of extensive usages of
this rifle in armed forces are; simple operation, light-weight, high
accuracy and efficiency. This machine gun is infantry support gun
normally fired from its bipod mount, however it can be installed in
tripod and is used in the classic role of a heavy machine gun to
provide long-range area fire and cover final protective lines at range
of 1000 meters.


7.62 mm MACHIN GUN
The
MGA3 is an open fully automatic weapon for sustained firing or firing
in bursts. It can be employed by all arms of services, army, navy, air
force for combating point and area targets.The weapon may be used as
standard machine gun for different purposes, when employed with the
bipod it is designated as a light machine gun (LMG). When used with
mount is designated
Tripod as a heavy machine gun (HMG). special mountings are available
for installation on vehicles, armoured vehicles & aircrafts.


The
mechanism of RPG 7 sub-rifle (training aid) expedites the training for
operating RPG 7 in military exercises in order to facilitate different
process such as operation, loading, targeting & firing. Preferences
are considered: reduction in expenses, increase in safety during
firing, creating the main firing conditions, cross leveling, loading,
adjustment, firing from a distance of 200 m without any accessories.


1/4ton Tactical Jeep
Double
differential, 1/4 ton tactical (Thunder Jeep) A four-door tactical jeep
with suitable equipment for different requirements of headquarters and
operational units of armed forces with special capabilities.


3/4ton Tactical Vehicle
3/4ton Tactical Vehicle


1 , 1/4 Ton Tactical Vehicle
Equipped
with two speed transfer case and mechanical engagement system. 4WD,
With differential lock. Driver cab. Equipped with suspension system
including leaf spring and telescopic shock absorber. Hard and soft top,
folding wind screen. Having two war and civil lighting systems.


Rakhsh 4x4 Wheeled Apc
Characterized
by high speed on road and excellent off-road mobility, The vehicle can
transport 10 men. The vehicle
is fitted with a 12.7mm
Automatic Gun and
can be fitted with different cupolas for various types of armaments.
The crew can see and fire through 10 vision blocks and firing ports and
can be quickly embarked or deployed through one rear door and two side
doors. Specific Equipment Central inflating system Run flat system
Winch Differential lock Air condition system.Option Equipment
Ceramic-composite layer Protection
against 12.7mm Up to14.5 mm Smoke
discharger and N.B.C protection
system.




Infantry Combat Vehicle Bmp-2
This
infantry combat vehicle is a full- tracked and highly mobile, provided
with armaments and armoured protection. The purpose of the vehicle is
to increase mobility, to improve power of fire and protection of
infantry that operates in the battle field under the conditions when
nuclear and missile weapons are used. The vehicle is equipped with 30
mm automatic gun 2A42 with double-belt feed. The gun is
stabilized in
two planes. The vehicle is also equipped with a 7.62-mm PKT machine
gun, mounted coaxially with the gun and a launcher for fighting against
the armoured targets from and outside the vehicle. The armament mounted
in the infantry combat vehicle enables the vehicle to fight against
different targets including tanks and combat helicopters. The vehicle
is also equipped with NBC
system for protection of the crew and
equipment inside the vehicle from the shock wave and penetrating
nuclear radiation of an explosion of nuclear ammunition, for protection
from the chemical and bacteriological weapons, and also for protection
of the crew from
radioactive dust when moving over contaminated terrain. To lay the
smoke screen for concealment, the vehicle is equipped with smoke -
generating equipment and smoke grenade launching system. BMP-2 can
cross water obstacles afloat using the track assembly for the purpose.
The vehicle can also be used for air landing. The personnel capacity of
the vehicle is ten consisting of three crew members (
commander, driver
and gunner-missile operator ) and seven troop.


Cobra BMT-2 APC
The
Iranian Cobra or BMT-2 armored
personnel carrier appearss to be an
indigenous design armed with a 30 mm gun or the ZU-23-2 anti-aircraft
gun—a light automatic weapons system that Iran has been manufacturing
for some years. Like the Zulfiqar main battle tank, the Cobra has been
undergoing field trials in Iranian military exercises since May 1996.
In late July 1997 Iranian President Hashemi Rafsanjani of Iran formally
inaugurated a production line for the domestically manufactured
Zulfiqar main battle tanks and Boragh tracked armoured personnel
carriers. The facility will also produce the BMT-2 personnel carrier
identified.
Boragh
The Chinese version of the BMP-1 is called the WZ 501. The WZ501 family
is a derivative of the the Soviet BMP-1, with a slight reduction in
weight and maximum road speed. It features a similar low pressure 73mm
gun and the Sagger ATGM, along with six roadwheels per side. The Type
86 IFV is fully amphibious and is fitted with an NBC system and
infra-red night vision equipments for commander, driver, and gunner.
China maintains roughly 1,000 Type-86 IFV's in operation. Variants
WZ501 (BMP-1) IFV 73mm gun, Red Arrow 73 (ATGM)
WZ503 (WZ501) No turret, taller hull Type
WZ504 (WZ501) ATGM Red Arrow 73
WZ505 (WZ501) Armored Ambulance - Raised rear compartment
WZ506 (WZ503) Armored Command Post (4 radios)
Boragh - Iranian-made
modification of the Chinese Type WZ 501/503 armored infantry fighting
vehicle. It was reported in early May 2002, that three additional
variations of the Boragh had been unveiled by the Iranian Defence
Industries Organisation (DIO) of Iran's Vehicle and Equipments Group
(VEIG). These consisted of a 120mm self-propelled mortar variant, of an
ammunition resupply vehicle and of an APC fitted with improved
armaments.
Specifications
Combat Weight 13,300 kg
Max Road Speed 65 km/h
Power to Weight Ratio 22 hp/ton
Height 2.16 m
Crew 3 + 8
BORAQ SUSPENSION SYSTEM
The vehicle is full-tracked and relatively light wich with high
movement and travel ability can be used in various combat operations.
This vehicle is equipped with suspension system, which is very suitable
for all regions especially for sandy roads. Track rubbers prevent
damages on the asphalt roads. Also, sprocket rubbers cause elimination
of track noises.
BORAQ ENGINE
According to Boraq users one of the most important features ofThe
Iranian Zulfiqar [Zolfaqar] main battle tank is believed to be
pieced together or developed from major components of the Russian T-72
and American M48 and M60 tanks. This tank, which is claimed to be in
production in Irana, is said to be similiar in configuration to the
M-48 and M-60. Other reports suggest that it bears a close resemblance
to the American M1 Abrams.
HULL OF BORAQ
Hull of Boraq with low height and suitable angles can be protected
against different armaments. Hull design provides complete safety
conditions and enough space for the comfort of troop.
ARMAMENT
This vehicle is convenient for movement of troop & capable to shoot
either from back portions or the vehicle side firing ports, therefore
12.7mm Dushka machine gun with 360
azimuth angle is equipped.
BORAQ FAMILY
Different types of Boraq vehicle family includes: Commander, Ambulance,
Engineering, Ammunition, Tow Missile Launchers, Mortar, Gunned and
different naval families.
TRAINING & OPERATION
One of the advantages of this vehicle is its easy training and
operating. Also simplicity and considering ergonomics parameters in the
vehicle design allows it to be repaired and maintained conveniently and
with low cost.



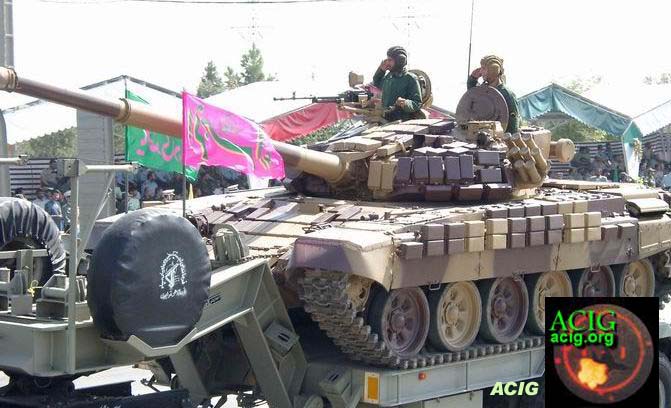
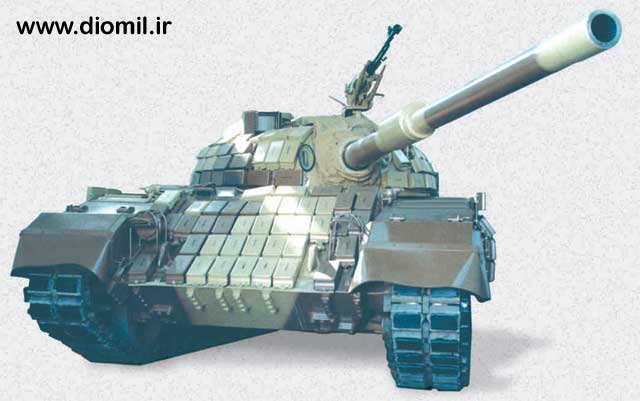
Zulfiqar
Tank




One of the features of the Zolfaqar tank which has drawn the attention
of the Defense Ministry is that indigenously-made parts have been used
in it. The testing prototypes of the tank were tested in 1993. Six
semi-industrial prototypes of the tank were produced and tested in
1997.
In April 1997 Acting Commander of the Ground Forces of the Iranian
Army, Lieutenant General Mohammad Reza Ashtiani announced that the mass
production of Zulfiqar tanks, which began in 1996, was still in
progress. He stated that the manufacture of 520 different kinds of tank
parts, 600 artillery parts, repair of 500 tanks and armored vehicles
have been carried out. In late July 1997 Iranian President Hashemi
Rafsanjani of Iran formally inaugurated a production line for the
domestically manufactured Zulfiqar main battle tanks and Boragh tracked
armoured personnel carriers. The facility, the Shahid Kolah Dooz
Industrial Complex, will also produce the BMT-2 personnel carrier
identified.
The Iranian tank is armed with a 125mm smoothbore gun fitted with a
fume extractor which may be fed from an automatic loader. It is known
that the Zulfiqar uses suspension like that fitted to Western MBTs such
as the M48/M60 MBT. The diesel engine is not taken from the T-72 since
this has a distinct exhaust outlet on the left side of the hull. This
feature is absent on the Zulfiqar.
The most recent T-72 is the 'S' version. The T-72S MBT weighs 44.5
tonnes and is armed with the latest stabilized 125mm smoothbore 2A46M
gun, IA40-1 computerised fire-control system (FCS) with laser
rangefinder and day/image intensification night sighting system. As
well as firing the normal types of 125mm separate-loading ammunition
(projectile and charge), the T-72S can also fire a Svir 9M119 (NATO
designation AT-11 'Sniper') laser beam-riding guided projectile to a
range of 4,000m. The T-72S is powered by the V-84MS diesel engine,
which develops 840hp and, with a combat weight of 44.5 tonnes, a
power-to-weight ratio of 18.87hp/tonne is obtained. For greater
cross-country mobility, the suspension has also been upgraded and mine
protection improved.
T-72Z An upgrade has been developed in Iran called the Type 72Z in
order to extend the operational life of the T-54/T-55 MBTs, and the
similar Chinese Type 59 equivalent used by Iran, all of which are armed
with a 100mm gun.
The existing 100mm gun has been replaced by a 105mm M68 rifled tank gun
in service with Iran on the M60A1 MBT. The Armament Industries Division
of the DIO probably makes this weapon because for some years it has had
the capability to bore tank and artillery barrels, such as the 122mm
Russian D-30.
To improve first-round hit probability, the Type 72Z has a Slovenian
Fontana EFCS-3 computerised FCS. According to the manufacturer,
installation of the EFCS-3 FCS enables stationary or moving targets to
be engaged while the Type T72Z MBT is static or moving.
The 7.62mm co-axial and roof-mounted 12.7mm machine guns have been
retained as has the ability to lay a smoke screen by injecting diesel
fuel into the exhaust outlet on the left of the hull. In addition, four
electrically operated smoke-grenade dischargers have been mounted on
each side of the turret.
At least one example of the Type 72Z has been fitted with a
roof-mounted laser warning device, probably coupled to a commander's
display and the electrically operated smoke-grenade launchers either
side of the turret.
Iranian sources say the upgraded Type 72Z is powered by the V-46-6 V-12
diesel engine developing 780hp. This engine has been integrated into a
new powerpack, which also includes the SPAT 1200 transmission for use
in automatic or semi-automatic modes. The V-46 V-12 diesel engine is
also installed in early production T-72 series MBTs, such as the T-72
and T-72A, and Iran could obtain these from various sources besides
Russia.
The Type 72Z's combat weight is quoted as 36 tonnes, power-to-weight
ratio 21.66hp/tonne and maximum road speed is 65km/h. This compares
with the T-55 MBT, which has a power-to-weight ratio of 16.11hp/tonne
and a maximum road speed of 50km/h. Last year, the Shahid Kolah Dooz
Industrial Complex revealed it had developed a new ERA package that can
be rapidly fixed to the T-54/ T-55, T-72 and other MBTs to improve
battlefield survivability against chemical energy (CE) and kinetic
energy (KE) attack. This Iranian ERA package is similar to that being
made and marketed by Russia and has been installed on Russian MBTs,
such as the T-80BV, for some years. The Iranian ERA armour system
comprises one composite layer. This protects against KE and CE
projectiles and an extra energetic material that provides protection
against KE attack. Iranian sources said this system can be dropped from
a height of 5m; will not be activated from small arms fire up to 30mm
in calibre or grenades; and is resistant to napalm type weapons.
this
vehicle is high mobility and power of the engine. Due to installation
of the engine with high movement power in comparison with other
full-tracked vehicles, it enjoys very suitable acceleration and speed.
The engine is air-cooled with 330 h/p.
It can produce power-to weight ratio up to 25.38 hp/ton. The quick
assembly and dismantling in fighting operations take less than 60
minutes.
Zulfiqar MBT
Early in 1994, Iran unveiled a new MBT called the Zulfigar which has
been developed by 'Construction Crusade', an arm of the Islamic
Revolutionary Guards Corps.
Russia is known to have provided Iran with a quantity of T-72 MBTs and
recent reports have indicated that the Zulfigar uses some components of
the Russian T-72 including the 125 mm smoothbore gun and automatic
loader. The T-72S, which Is an export version of the T-72 and is fitted
with ERA, is now being manufactured in Iran under license.
A detailed analysis of available information and photographs of the
Zulfiqar reveal that the hull and turret are of welded steel
construction and bear little resemblance to the T-72 at all.
The Russian T-72 MBT, like the earlier T-54/T-55/ T-62, is powered by a
diesel engine with the air Intakes/ outlets in the hull roof and the
single exhaust outlet on the left side of the hull towards the rear.
The new Iranian MBT is powered by a diesel engine with two exhaust
outlets in the rear of the hull; this could indicate the engine is a
V-type. The layout of the Zulfigar MBT is conventional with the driver
front left, turret in the centre and the power pack at the rear. The
driver has a single-piece hatch cover that opens to the right and three
day periscopes for driving when closed up. Suspension appears to be of
the torsion bar type with six dual rubber-tired roadwheels, idler at
the front and large drive sprocket at the rear; there are five return
rollers.
The roadwheels and other parts of the suspension appear to be very
similar to those of the US M60 series MBT which has been in service
with Iran for many years. The hull of the Iranian MBT is of the box
shape rather than the boat shape of the M48/M60 series.
The front of the turret is well sloped and is angled to the rear to
provide the maximum possible level of protection. There is a domed
ventilator in the turret roof on the right side and this is similar to
that fitted to the US M48/M60 series MBTs, as are the day/night driving
lights mounted on the glacis plate.
The commander is seated on the right with the gunner on the left. The
two examples of the Zulfiqar do have a number of minor differences in
the commander's cupola. The first one is similar to that used in the
T-72 while the second one has a cupola that is similar to that
developed in Israel and has an externally mounted 12.7 mm MG.
Main armament comprises a 125 mm smoothbore gun which is fitted with a
fume extractor and may well be fed by an automatic loader. The 125 mm
gun is positioned in a very narrow mantlet and there does not appear to
be a coaxial machine gun fitted.
Iran may well have the capability to assemble an MBT, but it must be
considered very doubtful if every single component used in the Zulfigar
is produced in Iran. Some key subsystems must still be imported. No
detailed specifications of the Zulfigar have been released but Iran
sources have stated that it has a combat weight of 40 tonnes, is
powered by a 1,000 hp diesel and has a maximum road speed of 70 km/h.
Iranian sources also claim that the Zulfigar is fitted with a weapon
stabilization system and a computerized fire-control system which
includes a laser range-finder. Night vision equipment is also fitted.
Late in 1999, it was stated that development of the third-generation
Zulfiqar MBT had been completed and volume production for the Iranian
ground forces had commenced.
Since the existence of the Zulfiqar MBT was first revealed in 1994,
further development has taken place with the latest version claimed to
have fundamental differences, especially in the turret.
According to Iran, the Zulfigar MBT features an NBC system, good
cross-country mobility, advanced fire control system (possibly of
European origin) and laser range-finder for improved first round hit
capability and reinforced passive armor.
It is believed that the 125 mm smooth bore gun and its associated
automatic loading system is the same as that installed in the T-72S MBT
which is now being manufactured in Iran under a deal signed with Russia
several years ago. This feeds the 125 mm projectile and then the charge
into the 125 mm gun. A 7.62 mm machine gun is mounted coaxial with the
main armament.
Russia and Poland have also supplied Iran with about 200 T-72 series
MBTs which were delivered between 1993 and 1995. In many respects the
Zulfigar MBT is very similar in. appearance to the now defunct
Brazilian ENGESA Osorio MBT but with suspension similar to that of the
105 mm armed M60 MBT already in service with Iran. Prototypes of the
Osorio were armed with a 105 mm rifled tank gun or a 120 mm smoothbore
gun, both of which were manually loaded.
It is believed that the power pack of the Zulfiqar MBT may also be used
in the upgraded Iranian T-54/T-55/ Type 59 MBT which is also called the
Type 72Z and covered in a separate entry. This consists of a Russian
V-46-6 V-12 diesel developing 780 hp coupled to a SPAT 1200
transmission. This gives Zulfiqar a maximum road speed of 65 km/h.
Status
In production. In service with the Iranian Army. There are no known
exports of the Zulfiqar.
Manufacturers
Defence Industries Organisation. Shahid Kolah Dooz Industrial Complex.
T-72Z
Safir-74
Iran has developed a new explosive reactive armour (ERA) package that
can be fitted to existing or new build MBTs to provide protection
against kinetic and high-explosive anti-tank projectiles. If fitted to
existing Iranian MBTs it would considerably increase their battlefield
survivability.
Type 72Z is a modernized version of T series tanks which is up-graded
by D.I.O. High combat performance of this tank can be defined by its
very high and accurate fire power, very good maneuverability (mobility)
and proper armour protection.Mounting a new armament system consisting
of :105mm barrel gun model M68 with a long operational life, effective
range, precision, high
firing power and simple replacement without removal of the
turret.Electronic Fire Control System (EFCS-3), as one of the most
advanced fire control systems makes Type 72Z enjoy a high combat firing
power in different condition of tank and targets at day and
night:Optimum chance to hit the target within a short
time.Automatic/manual stabilizing and firing the gun.Capability of
firing from mobile tank at moving or stable target.Using V46-6 engine
with 780 h.p, Type 72Z performs ideal acceleration and speed. Easy
driving and maneuverability can be increased with semi-automatic and
automatic gear shifting modes. Installation of all power compartment
that is : engine, gear box, brake, steering, transfer case, cooling
system and hydraulic system in an assembly called
“power
pack� have ensured lower repair time,
quick mounting and
dismantling of power pack. By employing armour reactive protection
boxes on this tank, protection against antitank weapons is increased.


Tosan Tank
In
December 1997 it was reported that Iran has manufactured a light battle
tank that it intends to mass produce in the near future for
unconventional warfare. Named Tosan [Towan] [Wild Horse
or Fury], the tank is said to be capable of rapid response and built
for strategic missions. Tosan is
equipped with a 90 mm gun, an imrproved firing and targeting system and
does not require special trucks to carry it. Iran claims it is nearly
self-sufficient in arms.
Khalid (Chieftain)
Information:
Designation: Chieftain
Contractor: BAe Systems Land Systems, Newcastle-upon-Tyne, UK
Country of Origin: Britain
Service Year: 1971
Type: Main Battle Tank
Crew: 4
Performance:
Powerplant: 1 x Leyland L60 2-stroke 6-cylinder multi-fuel engine with
an output of 750 hp.
Max Speed: 30 mph (48 km/h)
Range*: 280 miles (450 km)
*Indicates road range for vehicles or maximum lethal range for
towed-artillery systems.
Support Systems:
NBC System: Yes
Night Vision: Yes
Dimensions:
Length: 25 ft (7.52 m)
Width: 11.5 ft (3.50 m)
Height: 9.5 ft (2.90 m)
Weight: 53.3 tons (53,300 kg)
Armament:
1 x 120mm Main Gun
1 x 12.7mm RMG
1 x 7.62mm Coaxial Machine Gun
1 x 7.62mm Machine Gun
2 x 6 Smoke Grenade Dischargers
Ammunition:
64 x 120mm projectiles
300 x 12.7mm ammunition
6,000 x 7.62mm ammunition
12 x Smoke Grenades
Production Notes:
The Chieftain was developed in 1959 and saw production commence in
1971. The solid, if unspectacular, weapon system utilized conventional
doctrine in its design. The main gun can fire a variety of standard and
specialty rounds and was modified to support a computerized fire
control system and main gun stabilization.
The Chieftain was removed from frontline service as a main battle tank
in 1996. It still serves in some capacities as a battlefield recovery,
engineering, mine-clearing and bridgelayer vehicle variants as the
chassis has proved to be extremely adaptable.
Known Variants:
Mk 3/3P - Export Variant (Iran)
Shir 1 (now the 'Khalid') - Modified
Chieftain (Iran)
Mk 5/3P - Export Variant (Iran)
Chieftain ARV - Armored Reconnaissance Vehicle
Chieftain AARV - Armored Reconnaissance Vehicle
Chieftain AVLB - Bridgelayer
Chieftain AVRE
Known Operators:
Iran and Jordan.

One of the few IRIAS exponates was this re-worked Chieftain MBT, named
Mobarez ("Challenger"), with
some new armour on the side, and
re-engined with a more powerful engine based on US-technology.

Thunder 1 Artillery
In
May 1996, Iran claimed to have successfully tested its first locally
made self-propelled gun, the 122
mm Thunder 1. This vehicle is
apparently a modification of a Russian 122 mm gun, with a firing range
of 15,200 meters and a road speed of 65 kilometers per hour.
It may use
the Iranian-made Boragh chassis, a modification of the Chinese Type WZ
501/503 armored infantry fighting vehicle.
Raad-2 / Thunder 2 Artillery
In
early September 1997 it was reported that Iran had successfully tested
a locally built rapid fire mobile field gun known as "Thunder 2." The
Defense Industries Organization claimed that the 155 mm self-propelled
gun had a high firing rate, accuracy and mobility. It was described as
being able to fire five rounds per minute and move with a speed of 70
km (43 miles) per hour in the battlefield. The gun's range
was reported
as 30 km (19
miles), and it also includes features such as a laser
range-finder and a semi-automatic loading system.
Raad - 2 155 mm self- propelled gun- howitzer is an armoured tracked
vehicle designed and manufactured by D.I.O. The engine is located in
front of the vehicle. There are 5
crew including commander,
gunner,
driver, and two ammunition loaders. The hull and the
turret are made of
all welded special alloy steel and provide enough space for the crew to
operate freely.
Raad-2 is equipped with automatic laying system, direct
fire telescope,
night vision device, NBC protection system, automatic and manual fire
extinguishing equipment, radio & digital communication, gunner
& commander , s control panel and display, GPS & air
conditioner system.The engine is multi-fuel with high power to weight
ratio.